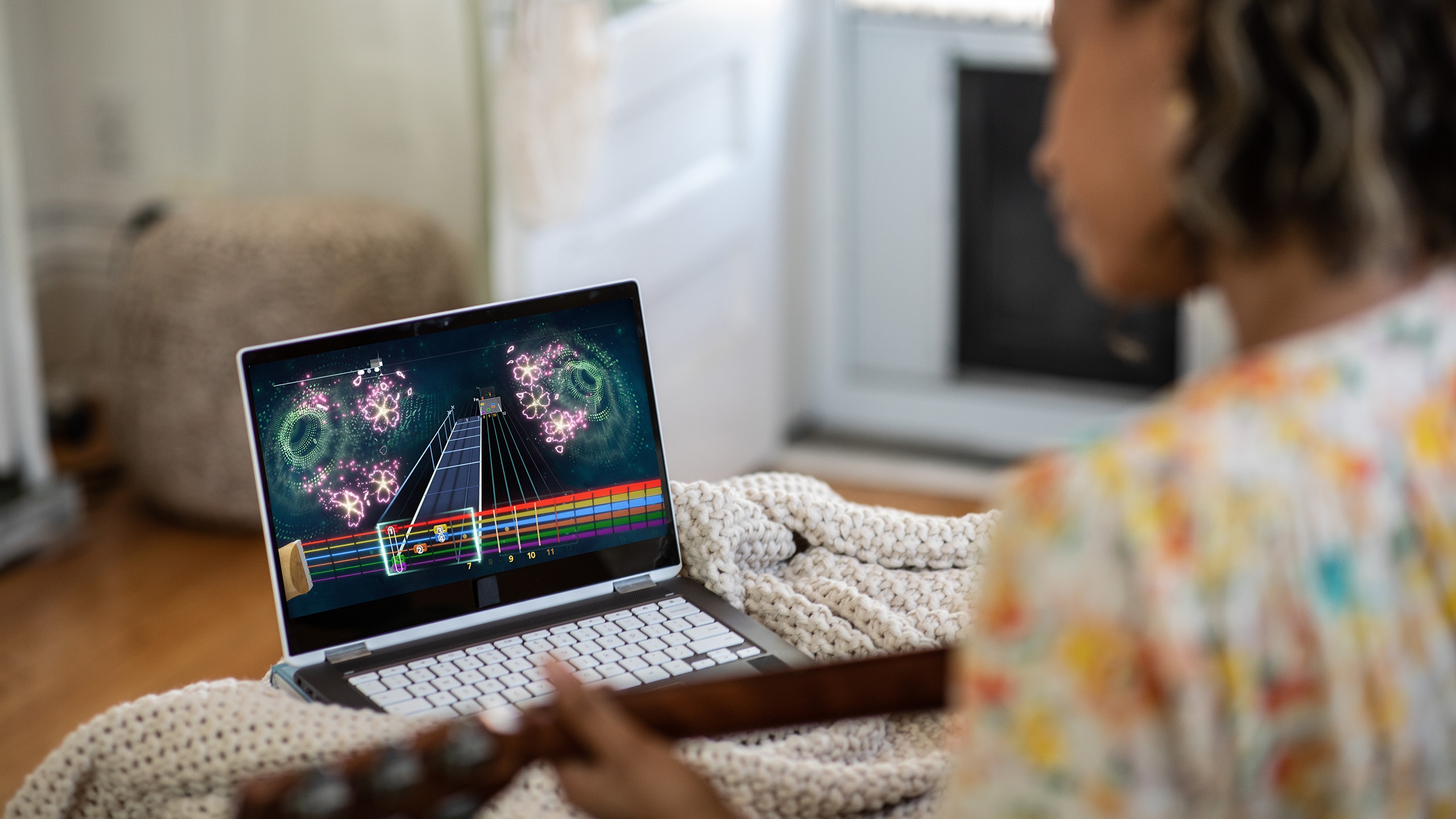
Fingerstyle guitar is a unique and expressive technique that enables musicians to create intricate melodies and rich harmonies. Unlike traditional guitar playing, where a pick might be used to strum or pluck the strings, fingerstyle involves using the fingertips or fingernails to pluck individual strings.
The result is a sound that can be both delicate and powerful, allowing for a wide range of musical expression. This article will delve into the fascinating history of fingerstyle guitar, explore where it has been and continues to be popularized, provide insights on how to get started with this playing style, and offer tips and tricks for those looking to master the technique.
What Is the History of Fingerstyle Guitar?
The origins of fingerstyle guitar can be traced back to classical guitar traditions, where musicians needed to play multiple musical lines simultaneously. By using individual fingers to pluck separate strings, classical guitarists were able to create complex polyphonic textures that made the guitar sound almost like a small orchestra.
In the folk music traditions of various cultures, fingerstyle also found a home. Musicians in places like Africa and South America developed their own unique fingerstyle techniques, often on instruments that were precursors to the modern guitar. These techniques allowed them to accompany themselves with intricate rhythms and melodies as they sang.
Throughout the 20th century, fingerstyle guitar began to evolve and spread into other musical genres. Influential musicians such as Merle Travis, Chet Atkins, and Mississippi John Hurt adapted fingerstyle to blues, country, and jazz music, creating new styles that were both innovative and rooted in tradition. Their contributions have left a lasting impact, paving the way for contemporary artists who continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with fingerstyle guitar.
In the modern era, fingerstyle has been embraced by a wide array of musicians across genres, from rock to pop, and has become a vital part of the global musical landscape. Its versatility and expressive power make it a favored technique for solo performers and ensemble players alike.
The history of fingerstyle guitar is a rich tapestry that weaves together various musical traditions, innovations, and individual artistry. It reflects a constant desire to explore and expand the expressive possibilities of the guitar, making it a continually relevant and exciting part of the musical world. Whether you're a seasoned guitarist looking to explore new techniques or a beginner intrigued by the sound of fingerstyle, understanding its history offers a deeper appreciation for the art and craft of this remarkable playing style.
How Does Fingerstyle Come Into Play Across Musical Genres?
![[RS+] News - What Is Fingerstyle Guitar? - img](http://staticctf.ubisoft.com/J3yJr34U2pZ2Ieem48Dwy9uqj5PNUQTn/nq1gtOPKvjz6J9IWE4mKs/2f6264ee5a1fb43933f525fc7f13782d/finger2.jpg)
Fingerstyle guitar is not confined to a single genre; rather, it has permeated various musical styles, adding its unique flavor to each.
Classical Guitar
In classical music, fingerstyle is at the heart of the technique. Composers like Francisco Tárrega and Fernando Sor wrote pieces that are still played today, showcasing the ability to weave multiple musical lines into a cohesive whole. Classical fingerstyle often requires precise finger placement and control, leading to beautifully articulated melodies and harmonies.
Folk and Country Music
Folk musicians around the world have adopted fingerstyle to create rhythmic accompaniments and melodic solos. In American country music, figures like Chet Atkins took fingerpicking to a new level, combining elements of blues, jazz, and traditional country sounds. This blend led to a distinctive style known as "Travis picking."
Jazz and Blues
Fingerstyle found a natural home in jazz and blues, with artists like Mississippi John Hurt and Wes Montgomery using their fingers to create swinging rhythms and soulful solos. In jazz, fingerstyle allows for intricate chord voicings and smooth melodic lines, enhancing the genre's complex harmonies.
Global Reach
Fingerstyle has been embraced by different cultures, adapting to various musical traditions. From Flamenco in Spain to the intricate Kora playing in West Africa, fingerstyle techniques have been shaped by local musical contexts, creating a rich tapestry of global guitar music.
What Are the Basics of Playing Fingerstyle?
Playing fingerstyle guitar can be both rewarding and challenging. Here's a guide to get you started:
-
String Plucking Techniques: Plucking can be done using the fingertips or fingernails, each producing a different tone. Experiment to find what feels comfortable and sounds best to you.
-
__Hand Positioning: __The "picking hand" typically rests near the soundhole, while the "fretting hand" presses the strings on the fretboard. This separation allows for independent movement, which is critical for playing different musical lines simultaneously.
-
Common Patterns: There are many fingerpicking patterns used in fingerstyle. Beginners might start by alternating between the thumb and other fingers, creating a simple but effective rhythm. More advanced patterns can involve complex syncopations and arpeggios.
-
Tuning Considerations: While standard tuning is common, some fingerstyle pieces require alternate tunings like Open G or Drop D. These tunings can create resonant open strings and unique chord voicings that enhance the musical piece.
The basics of fingerstyle open a world of creative possibilities. With practice and exploration, these fundamental techniques can lead to a deeply expressive and satisfying way to play the guitar. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced player looking to expand your skills, fingerstyle offers a rich and rewarding musical journey.
Is Fingerstyle Guitar Still Used In Music?
Fingerstyle guitar's popularity has spread across continents and musical cultures, and its influence continues to grow.
Here's an overview of where this technique has flourished:
-
North America: In the United States, fingerstyle has been popularized in genres like blues, country, and folk. Icons like Chet Atkins and Merle Travis have left a lasting legacy, and contemporary artists like Tommy Emmanuel continue to push the technique to new heights.
-
Europe: From classical guitar masters in Spain to folk musicians in the British Isles, fingerstyle has become a key part of European guitar traditions. Artists like Bert Jansch and John Renbourn have played a crucial role in popularizing the technique in the folk scene.
-
Asia: In recent years, Asia has become a hotspot for fingerstyle guitar. Musicians like Sungha Jung from South Korea have gained international fame, inspiring a new generation of guitarists to explore this technique.
-
Online Community: The internet has played a significant role in spreading fingerstyle guitar to a wider audience. YouTube channels, online lessons, and other web communities dedicated to fingerstyle can offer resources and inspiration for guitarists worldwide.
What Are Some Tips and Tricks for Playing Fingerstyle?
![[RS+] News - What Is Fingerstyle Guitar? - img 2](http://staticctf.ubisoft.com/J3yJr34U2pZ2Ieem48Dwy9uqj5PNUQTn/CQ6omyEE0sDsQwvUn32Zy/fe24b4861f162c69a0768f6005b8e6f0/finger3.jpg)
Starting your journey into fingerstyle guitar may seem daunting, but with the right approach and resources, it can be an enjoyable and fulfilling experience.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
-
__Choose the Right Guitar: __While fingerstyle can be played on any guitar, some guitars with wider necks and string spacing may be more comfortable for fingerpicking. Classical guitars, for example, are often preferred by beginners.
-
Learn Basic Techniques: Start with fundamental techniques like thumb and finger plucking, alternating bass lines, and simple arpeggios. There are plenty of online tutorials and books that can guide you.
-
Practice Simple Songs: Begin with songs that have straightforward fingerpicking patterns. Playing recognizable tunes can be motivating and fun.
-
Experiment with Tunings: While fingerstyle guitar is sometimes played in standard tuning, alternate tunings may allow more fluid chord shapes. Try out different tunings to find what resonates with you. Different tunings can inspire new musical ideas and enrich your playing.
-
Start Slow: Focus on accuracy and clarity before building speed. Use a metronome to practice at a comfortable pace, gradually increasing the tempo as you become more confident.
-
Explore Different Tunings: Alternate tunings can open new sonic possibilities. Experimenting with different tunings like Open G can inspire creativity and add depth to your playing.
-
Focus on Hand Independence: Fingerstyle requires coordination between the "picking hand" and the "fretting hand." Practice exercises that challenge you to play different rhythms and melodies simultaneously.
-
Study the Greats: Listening to and learning from fingerstyle masters can provide valuable insights into technique and musicality. Study their playing and try to understand what makes it unique.
-
Be Patient and Persistent: Like any complex skill, fingerstyle guitar requires dedication and practice. Keep a positive and patient attitude, set realistic goals, and enjoy the process of learning and growing as a musician.
Practice Daily
Fingerstyle guitar is an endlessly rewarding and multifaceted technique that offers opportunities for personal expression and growth. By understanding its history, recognizing its global influence, and practicing with focus and intention, you can embark on an exciting musical adventure that will enrich your playing and deepen your connection to the guitar. Whether you're new to fingerstyle or looking to refine your skills, these tips and insights provide a solid foundation for your musical journey.
For beginners and seasoned guitarists alike, learning fingerstyle opens up new horizons for personal creativity and musical exploration. Whether you're drawn to the intricate melodies of classical pieces, the soulful grooves of blues, or the rhythmic complexities of folk, there's a world of fingerstyle guitar waiting for you to discover.
While many songs can be transposed into fingerstyle guitar, learning to play in this style should start with simple songs. With more than 7,000 songs and genres from around the world, Rocksmith+ remains the best learning platform for learning new musical styles.
Sources:
History of Fingerstyle Technique | Fingerstyle Guitar
Spanish Music History | Enforex Spanish Culture
Francisco Tarrega | Maestros of the Guitar
How Long Does it Really Take to Learn Guitar? | Mighty Expert